Water mobility (as we like to call it) has managed to overtake electric mobility, and has made it clear that the future goes far beyond EVs. China still doesn’t want to believe it, and Japan is taking the lead. However, everything could change now with California’s latest strategy to change the hydrogen engine forever: they are clear on how to do it, and they are going to position us in front of the whole planet, with a project so futuristic that it is already causing concerns to the rest of the countries and carmakers.
California’s plans for the hydrogen engine: America is shocked (and experts are worried)
Starting with classic flex-fuels and ending up with cutting-edge hydrogen ICEs, California has been a pioneer in supporting the development of automobiles using non-fossil fuels. But the state-imposed emission requirements have also been a major barrier for hydrogen ICEs to be used across the state.
This situation has proved to be very unfavorable, with California’s stance against emissions affecting the prospects of hydrogen ICEs. The state’s regulations are mainly about the Zero-Emission Vehicle (ZEV) that covers battery-electric and hydrogen fuel cell cars. This has greatly impounded the uptake of hydrogen ICEs since they are not properly catered for as ZEVs.
The present and future of the U.S. market for hydrogen ICEs, therefore, very much depends on what California and the other 10 states that will implement the said emission standards intend to do. Due to the specified requirements of the state, the hydrogen ICEs may not be able to fulfill the requirements, thus implying the Denial of the use of the hydrogen ICEs in the broader U.S. market.
Shell’s decision to cease the utilization of seven hydrogen fueling stations that were originally established in California, particularly within the San Francisco Bay Area, has hampered the refueling opportunities for hydrogen fuel cell car owners. Currently, there are only 55 passenger hydrogen fuel stations in the state.
It’s not as easy as it sounds: California regulations could end it all
In addition, Shell has also ceased plans for constructing 48 new hydrogen fuel stations for passenger cars in California, even though the firm was awarded ample government subsidies in the calendar year 2020. This withdrawal is a drastic change from Shell’s previous interest in the hydrogen fueling sector in the United States, which began when Shell initiated the first pilot station in 2005.
There has been a bleaker outlook depicted for the relatively conservative U.S. market for hydrogen fuel cell small automobiles like passenger cars manufactured mainly by Japanese and the South Korean auto giants; Honda and Hyundai, respectively, due to a scarcity of hydrogen stations located predominantly in Greater Los Angeles and the San Francisco Bay Area.
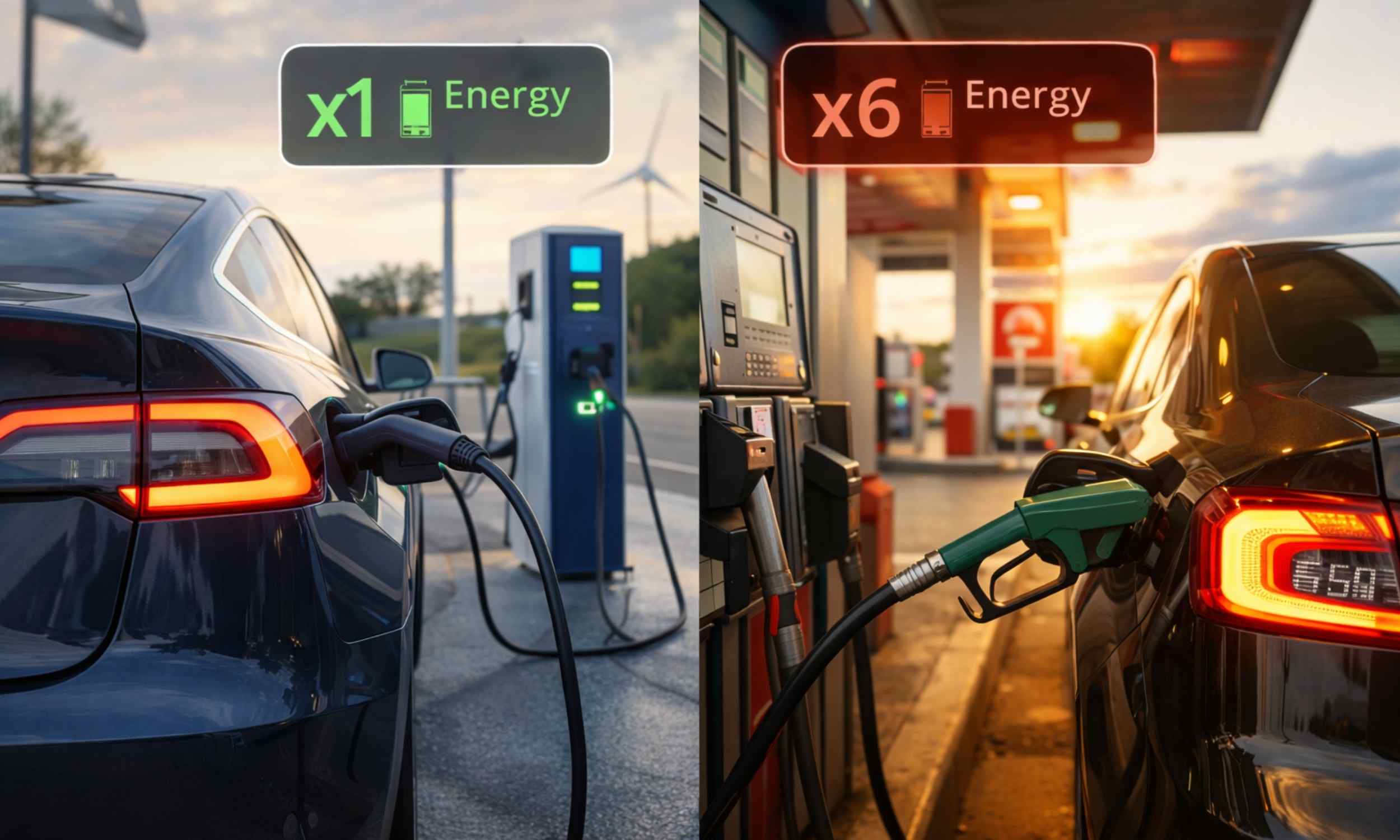
Some examples have appeared in the American automotive press that describe the problems of hydrogen stations in California since last summer: interruptions in supplies, high prices for hydrogen, their irregular working hours, and long queues for refueling.
As of January 2024, the number of hydrogen fuel cell passenger cars sold and lessened in California was still around 17,700.
California is clear on what to do with the hydrogen engine: 4 steps to take the lead from Japan
To support the growth of hydrogen-powered vehicles, California has enacted several laws and incentives:To support the growth of hydrogen-powered vehicles, California has enacted several laws and incentives:
- Hydrogen Fuel Specifications: The state’s Department of Food and Agriculture, Division of Measurement Standards, asks that hydrogen fuel used in internal combustion engines and fuel cells have to be of the SAE International J2719 kind.
- Hydrogen Fueling Station Evaluation: It is under the laws of CARB to determine the requirements for more new publicly accessible hydrogen fueling stations and present its decision to the said CEC. The CEC then disburses up to $20 million in a year to put up the necessary stations.
- Zero Emission Vehicle (ZEV) Promotion Plan: This has seen the state of California adopt steep targets aimed at promoting commercialization as well as the deployment of ZEVs at least by the year. Its targets are the concurrent introduction of:
- 5 million ZEVs on the road by 2025.
- 5 million by 2030.
- Alternative Fuel and Vehicle Policy Development: The CEC must file an Integrated Energy Policy Report with the Governor that should recommend military actions to enhance the deployment of ZEV structures.
Do you understand why California has a golden opportunity to take the lead in the hydrogen engine? America has lagged somewhat behind with the FCEV revolution, although we are among the leaders in the generation of this fuel in all its “colors” (some greener than others). This is a project that has a lot to prove to the rest of the world and for which, as you can imagine, Japan is watching us closely, with Toyota and Subaru following closely behind.