The Laser Interferometer Gravitational-wave Observatory (LIGO) machine project is one of the most successful scientific and technological initiatives of the relatively recent period that transformed the human understanding of the universe from the ground up.
Located in Hanford, Washington, and Livingston, Louisiana, supported by the National Science Foundation, and operated jointly by Caltech and MIT, LIGO has been reported to directly detect gravitational waves and thus confirm one of Einstein’s theories that spacetime can be bent.
The scientific community heralds this success as a breakthrough in gravitational-wave observations that have not been possible before. LIGO makes quantum and post-Newtonian physics significantly more accessible, and it has become a powerful tool in astronomy and physics, making this breakthrough possible.
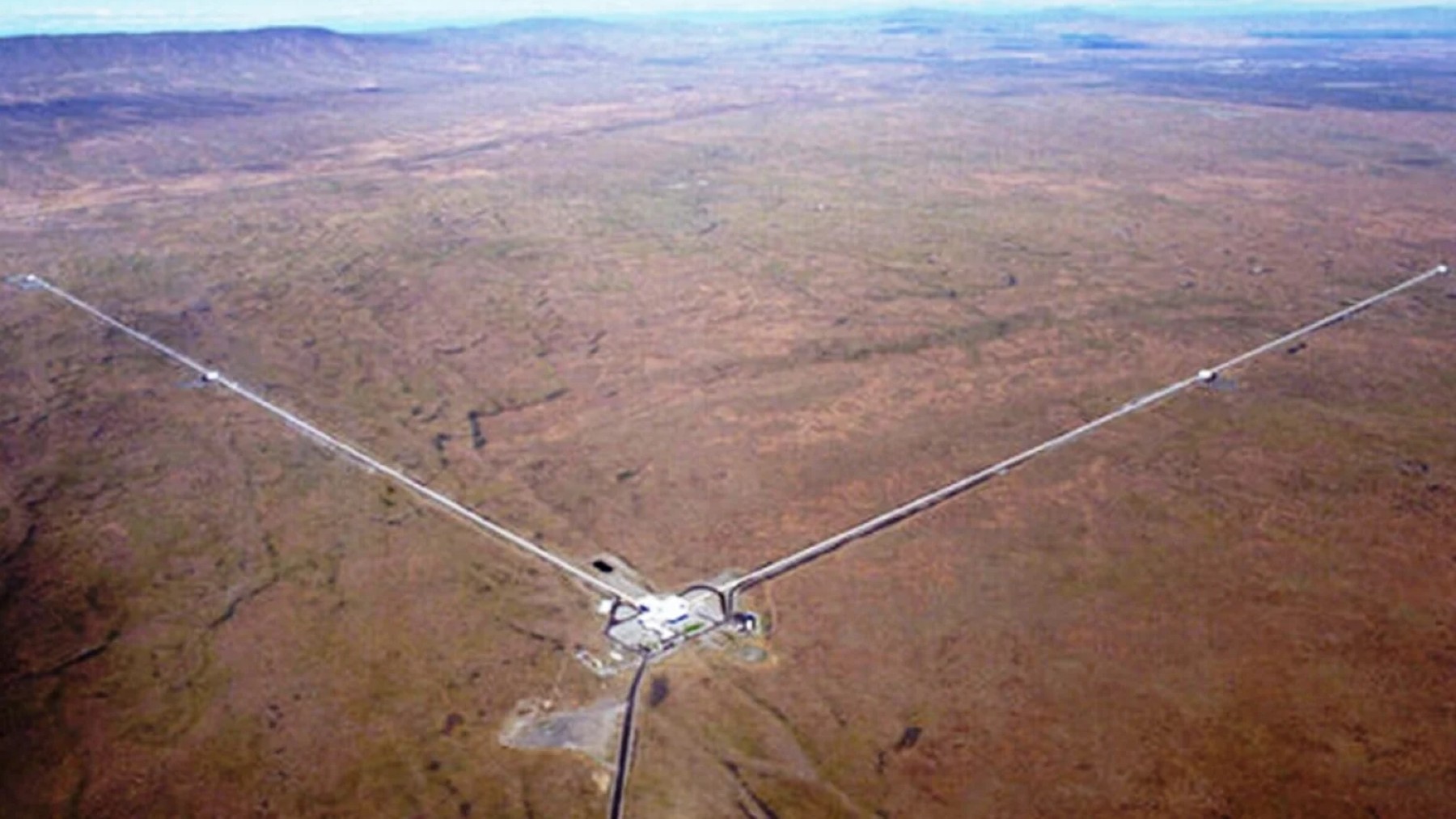
Inside the groundbreaking structure and design of the LIGO observatory facilities
LIGO is a massive interferometer comprising two detectors in Hanford, Washington, and the other in Livingston, Louisiana. The L-shaped interferometer includes a facility that is 4 kilometres in length for each arm of the facility. These instruments, such as an antenna, pick up even the slightest stimuli or deviations in spacetime that come with gravitational waves.
The setup implies having two detectors to confirm the signals and establish the provenance of gravitational waves more effectively. The positioning of these observatories in two distinct parts of the United States has various usages. It assists in filtering out local interference and offers a broad reference point from which to calculate the origins of gravitational waves.
This is how interferometry makes detecting cosmic phenomena possible with LIGO
Interferometry is the backbone of how LIGO functions, and in the next couple of subheadings, that aspect will be expounded on. A laser source is split in each interferometer, and a portion is sent to each perpendicular leg of the interferometer. The beams are reflected by the mirrors and combined again.
Accompanying these changes, the frequency of the laser interferes with changes in the arm’s length by passing a gravitational wave through the observatory. It alters the interference pattern that makes it possible to detect and measure the gravitational waves in precise measures, a distance smaller than a proton’s size.
The interferometry applied in LIGO is so exquisite that the meter scale interferometer can measure the changes in the arm length of 4 kilometres by a fraction lower than one part in ten-thousandth of the proton wavelength.
LIGO’s remarkable accomplishments and what the future holds for this project
LIGO has recorded many cosmic phenomena over three years after its official observation of gravitational waves in September 2015. A chart notes 90 drives of gravitational waves discovered between September 2015 and March 2020, proving this sphere’s fast development.
More recently, LIGO has been developing with further enhancements and plans to add sensitivity and observation modes. It also maintains the relevancy of LIGO in the gravitational wave field, allowing it to advance into discoveries about the universe.
The constant enhancement of the LIGO’s apparatus has ensured it detects more incidences and types, such as the neutron star that merged in 2017. This event generated gravitational waves and electromagnetic radiation, making it a part of multi-messenger astronomy.
LIGO’s ongoing evolution continues to unlock the mysteries of the universe
Hence, LIGO remains symbolic of the human spirit, which strives to incomprehension of the mysteries of the universe. LISA Pathfinder will extend the capabilities of its sister facility, LIGO, to confirm Einstein’s theories and provide a new means of observing the universe.
This positive outcome is due to the dynamism of the research project for the last few decades, technological advancement, and collaboration. In the future, as LIGO keeps expanding its horizons and making ever-new advancements, the secrets of the universe from the merging of black holes and neutron stars and perhaps other unknown cosmic events will be unlocked.
The ongoing work exemplified by LIGO is a suitable demonstration of the timeless pursuit of scientific pursuit and the ability of humanity to expand and augment the known universe, providing a promising light for future advancements in astrophysics and cosmology.
As stated earlier, it’s not only scientists who can benefit from the work of LIGO, but the discoveries of the binary black hole have prompted many people to take an interest in simple physics and the cosmos. It confirms that authoritarian long-term financing of fundamental scientific research can yield significant discoveries that would dramatically redefine our view of the universe and our role in it.