The Russian floating nuclear power station, the Akademik Lomonosov, produced 1 billion kilowatt-hours (kWh) of energy, and that has inspired both wonder and fear around the world. In this article, it is necessary to describe the specifics of this fantastic engineering structure and its outstanding performance characteristics and dangers.
The Akademik Lomonosov: a floating nuclear marvel that powers remote regions
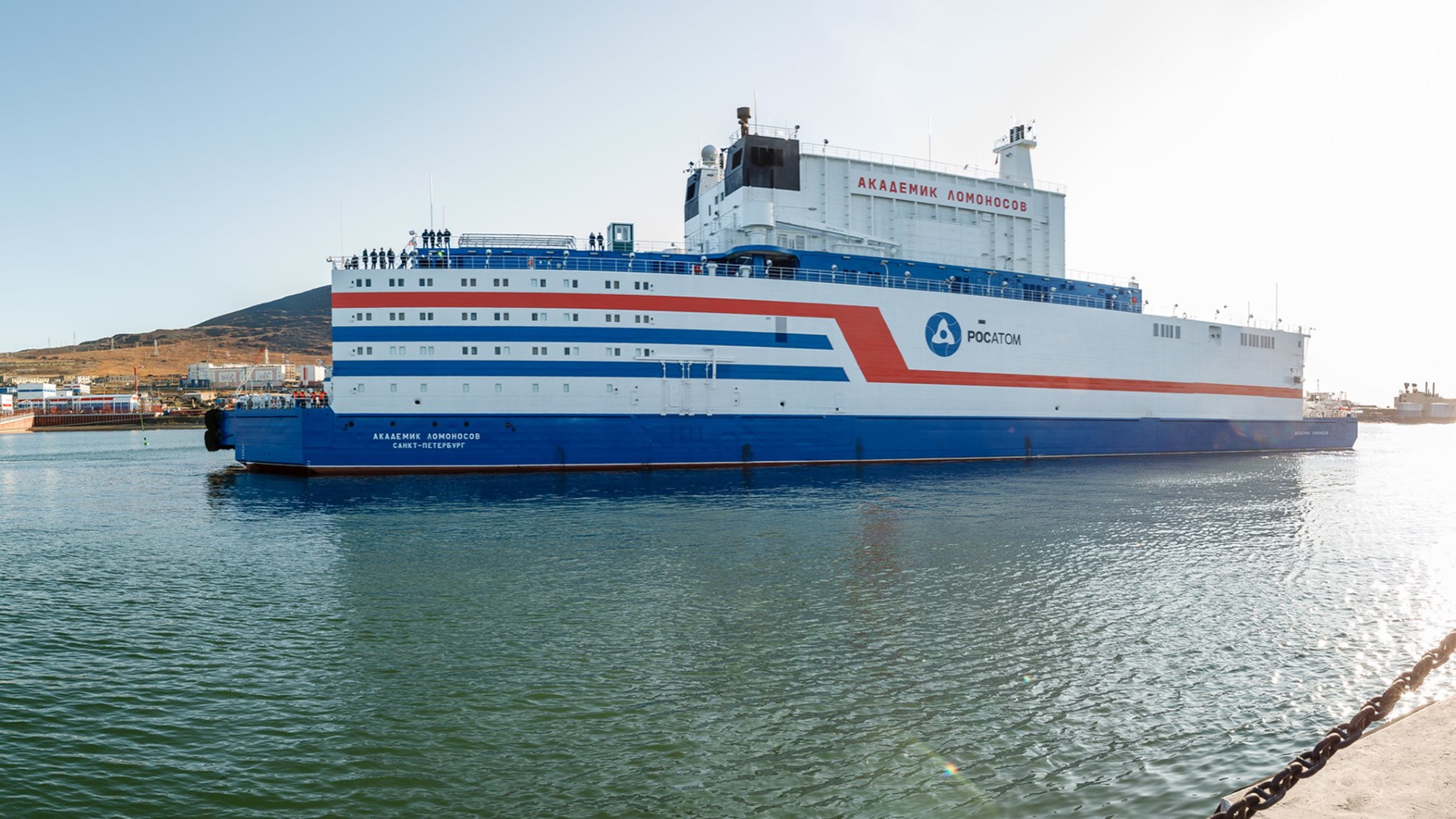
The Akademik Lomonosov, which has been in operation since May 2020, is said to be the only floating nuclear power plant globally. Located in the Russian Arctic port of Pevek, it operates as the northernmost heat and electricity supply source. The plant contains two units, the KLT-40S reactor, based on those used in Russian icebreakers, and its thermal power is 300 MW, of which the electrical power is approximately 70 MW.
Originally intended as the northern shipyard in Severodvinsk in the Russian Northwest region, the plant has been relocated to Pevek to substitute the obsolete Bilibino Nuclear Power Station. Akademik Lomonosov now accounts for more than 60% of the Chaun-Bilibino power hub load and greatly contributes to the electrification of the area.
Achieving 1 billion kWh: Akademik Lomonosov’s incredible energy milestone
In January 2025, the Akademik Lomonosov achieved another important aim to supply one billion kilowatt-hours of power. This accomplishment demonstrates the capacity of the plant to offer a stable and sufficient energy supply. The plant uses low-enriched uranium (LEU), and the fuel has been renewed in the two reactors after the first cycle.
The plant also helps convert waste heat into useful energy sources, as much as 60MW thermal for heating. Currently, it is designed for 5000 people, relates to mining and processing the Baimskaya ore area, and treats up to 240000 meters of seawater daily.
Operational risks and safety concerns: Is the Akademik Lomonosov a ticking time bomb?
As an extraordinary engineering accomplishment, Akademik Lomonosov raises numerous issues concerning its safety. Some environmental threats which are associated with the plant location in the Arctic region include extreme weather conditions and the incidence of environmental calamities. The fresh and spent nuclear fuel movement through the Northern Sea Route superimposes another level of complexity and danger.
Russian company Rosatom, responsible for the construction of the power plant, has taken adequate measures to ensure the plant’s safety. Receipt of fresh uranium fuel is done in special containers by Pevek, while the spent fuel is stored in the vessel so that it will be taken back to Murmansk to be reprocessed. However, it is recalled that the probability of accidents or unfavorable handling of such substances is still a possibility.
Global implications and future prospects: Is floating nuclear power the future?
The success that has been attained has led Rosatom to contemplate the possibility of assembling more Akademik Lomonosov type of floating nuclear power plants for export. These new plants would have a generation capacity of one hundred MWe apart from having a design life of well over sixty years. While this could help the issue in regions where energy is scarce, this creates problems about nuclear technology and the chances included.
Thus, achieving a billion kilowatt-hours of energy equals nuclear power’s usefulness for attaining the net-zero energy target. but nuclear fission’s safety and its impact on the environment will always remain a rather hot topic. The Akademik Lomonosov is representative of the complex interrelation between the efficient usage of atomic energy and the ability to prevent negative consequences of its application to people and the environment.
Akademik Lomonosov’s success and risks serve as a cautionary tale for the future
Thus, achieving the indicator of 1 billion kWh, the Akademik Lomonosov set a historical record in the nuclear energy sector. It makes Russia the holder of the only floating nuclear power station whose possibilities of delivering stable and large amounts of electricity can be reached with the help of nuclear technologies. However, such technology’s protective issues and ecological threats cannot be undermined.
Indeed, as Russia continues with feasibility studies of float nuclear power plants, the world should watch out for inherent dangers and ensure safety measures are implemented. This is the inspirational theme of the Akademik Lomonosov. The challenge of increasing energy demands globally should be another cautionary lesson regarding the use of nuclear energy.