As an epitome of engineering and synergy, SpaceX comes through with style and glamour by launching a mission to rescue two astronauts who have been on the International Space Station (ISS) since June. This mission shows the progress made in space exploration and the problems encountered in providing for the safety and recovery of astronauts in the context of the ongoing commercial space revolution.
Astronauts’ rescue from a high-risk mission: How Boeing’s struggles led to SpaceX stepping in
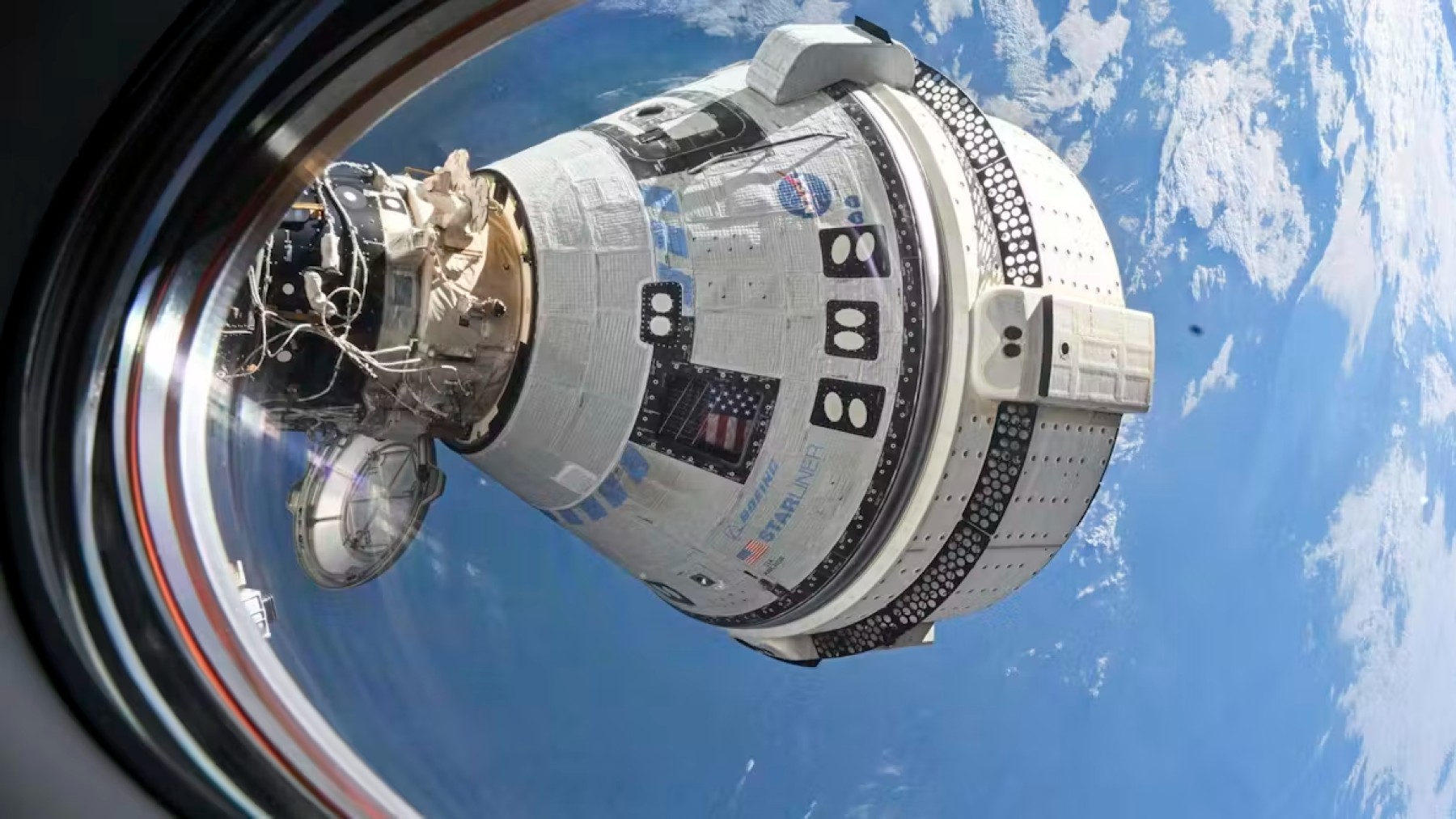
Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams are space-experienced astronauts who traveled to the ISS inside Boeing’s Starliner on June 5, and the mission was intended to last eight days. However, problems started developing when the Starliner began developing helium leaks before launching, and NASA had to go ahead with the mission in what could be regarded as high-risk. Whereas the first questions appeared tame, questions, after a capsule was in orbit, became more complicated and led to several thrusters failing during docking.
Because Boeing’s Starliner is still facing challenges and the astronauts cannot return as planned, NASA has a problem. The agency was forced to allow SpaceX to intercede and help Wilmore and Williams return safely to Earth. This decision highlights problems that Boeing has experienced in its Commercial Crew Program, which encountered multiple delays and technical issues, as to whether it can successfully challenge SpaceX, which conducts crewed missions.
SpaceX’s Crew Dragon spacecraft leads the rescue: A closer look at the evacuation process from ISS
In the case of the Starship, SpaceX planned to evacuate the stranded astronauts and the rest of the crew on September 28, 2024, using a Crew-9 mission launched from the Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. The two-person crew will be made of NASA astronaut Nick Hague and Roscosmos cosmonaut Aleksandr Gorbunov, who will spend five months in the ISS conducting experiments. The launch was an important event as it became the first human spaceflight mission from the new launchpad, proving the company’s further development of achievements in innovation and operation.
The Crew Dragon spacecraft Freedom was launched on top of the Falcon 9 rocket; nine engines were launched to lift the spacecraft, and once the orbiting speeds had been achieved, the craft detached from the rocket and started moving in the direction of the ISS using its built-in control rockets. Such attention to detail and engineering made for a microcosm of what’s come with commercial space travel, especially with SpaceX at the vanguard.
Before Hague and Gorbunov get to the ISS, the two will conduct various scientific experiments. Such research plans comprise the coagulation of blood, the impact of moisture on the growth of plants in space, and the alterations in the vision of space travelers for more extended space missions. Such research is vital for future long-duration missions, including those that require travel to Mars.
How collaboration between SpaceX and NASA shapes the future of human space travel and astronaut safety
The recent Crew-9 mission is a clear example of the need for cooperation in this line since it was successful. SpaceX and Boeing are privately built, but NASA is responsible for multi-agency contracts and astronaut protection as such firms progress. This mission proves the reliability of SpaceX services and opens up various questions about the further evolution of human space travel as the service market expands competitively.
Problems of Boeing with the Starliner have put this spacecraft under increased public pressure and require enhancing safety measures. However, NASA’s cooperation with SpaceX underlines the problem-solving collaboration in the space industry. That is why flexibility is essential in the agency, as situations are unpredictable, and complications may occur when handling the astronauts and the missions.
Overall, it is critical to regard SpaceX’s Crew-9 mission to save Wilmore and Williams as an important event in human spaceflight studies. It demonstrates that space agencies and some companies are ready to solve some problems and carry out space activities beyond the Earth. Turning our heads up at the sky, one will realize that cooperation and innovation will be core values in space exploration.