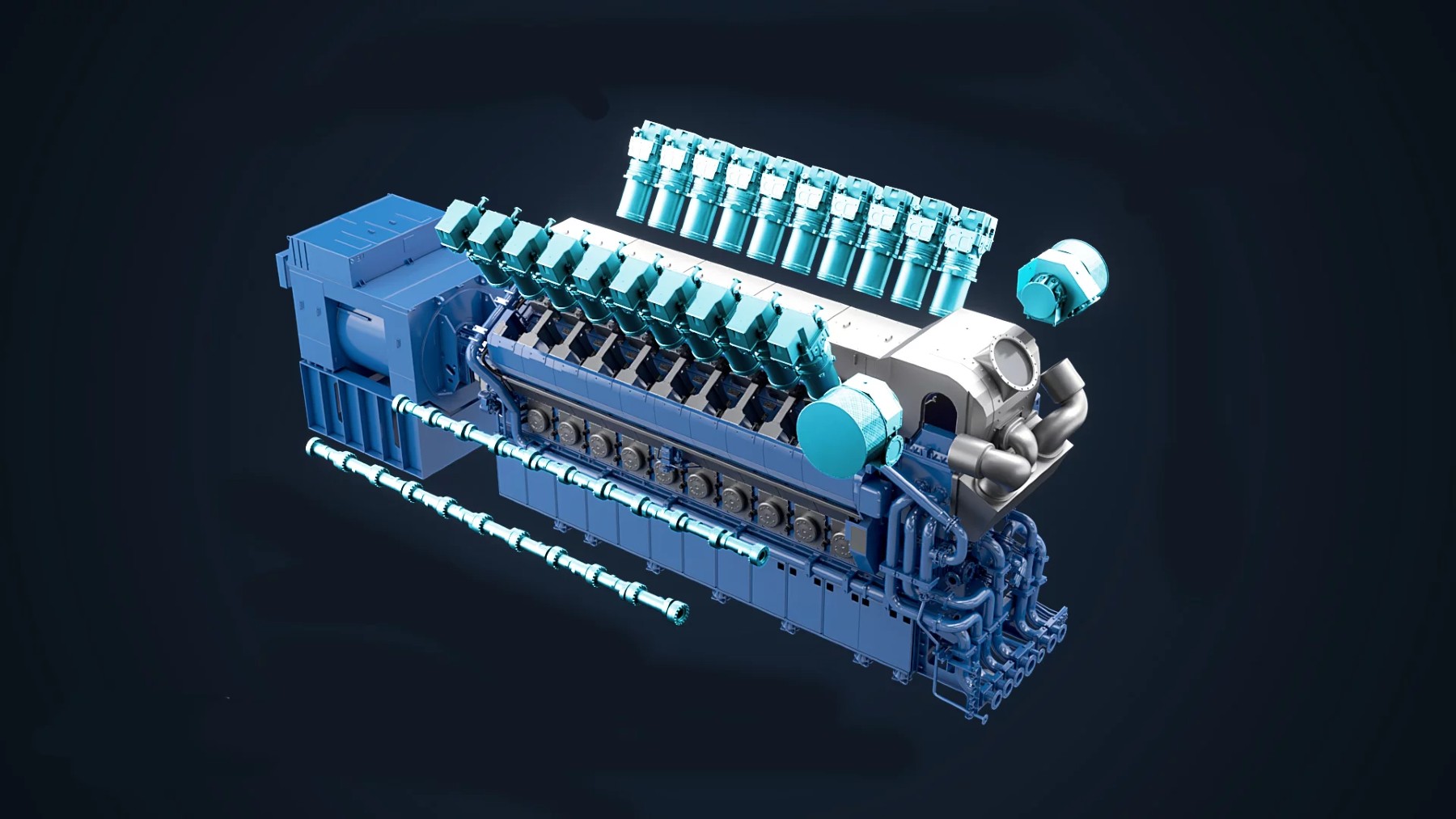
In a historic move, China’s Guangzhou Automobile Group Co. (GAC), which teamed up with Toyota, has revealed a 2 Otto-cycle 0-liter internal combustion engine that operates on liquid ammonia. GAC demonstrated this promising work at its annual technology conference, and it has made a great stride towards the use of new-generation fuels to lower its carbon footprint. Despite such flexibility, power, and environmental impacts, it is also rather risky and somewhat unrealistic as a daily car engine.
Revolutionizing green propulsion: New ammonia powered engine breakthrough revealed
The cooperation between GAC and Toyota has produced an ammonia-powered engine that delivers performance and environmental impact in a way that has not been seen before. This unique powerplant produces a healthy 161 horsepower and impressively 90% less CO2 emissions than traditional engines. It also eliminates the emission of CO2, hydrocarbons, and soot since combustion is carbon-free in the new generation of the engine, making a big step towards a greener transport network.
Through the discovery and utilization of ammonia, this technology has provided a way to minimize the environmental impact of internal combustion engines significantly. The successful development of this engine not only proves the possibility of the use of nonconventional fuels but also can give hope for change in the conventional fuels used in the automobile industry, thus providing a ray of hope towards more sustainable and environment-friendly mobility without compromising the power and performance.
Overcoming technical hurdles: Challenges facing ammonia as a new fuel alternative
However, ammonia also poses some technical hurdles that have to be overcome for the substance to become a feasible fuel for automobiles. It makes the fuel’s energy density somewhat around a third of that of diesel, meaning that either “larger fuel tanks or more frequent refueling to achieve comparable range” were required. Fuel with an octane rating of 120, in this case, ammonia, needs significant modifications in the engine for it to undergo full combustion in the shortest time possible.
These properties make it extremely challenging to ignite and combust ammonia properly within traditional engine configurations and architecture, thus representing a significant barrier to its integration into passenger cars without fundamental changes to the vehicles. It is important to deal with these technical challenges since ammonia can be considered a promising candidate for breakthroughs in the automotive field, at least as a feedstock material for producing other efficient fuels, at least at the present stage of technological development.
Addressing safety and infrastructure: Ammonia fuel brings new challenges
Ammonia as a fuel raises numerous new safety challenges and infrastructure concerns that would need to be addressed in the context of the ammonia revolution. Handling and storage of ammonia is very dangerous because this substance is toxic to both human beings and other animals.
As for the atmospheric changes, one might predict the changes in nitrogen emissions in the form of ammonia lead to secondary effects in the form of compounds such as ozone and ammonia, which are capable of resulting in consequences such as acid rain and toxic impact on the lungs.
Moreover, there needs to be an existing infrastructure for ammonia circulation and refueling, which poses a major challenge for passenger car applications of ammonia. These concerns and limitations are only soluble by obtaining extensive safety measures, sound regulatory standards, and, more importantly, establishing new systems of fueling and distribution.
These challenges best demonstrate that a broader synergistic approach with regard to the application of ammonia as a fuel must be used while taking into consideration the environmental advantages of the given fuel, as well as risks referring to public safety and the construction of the requisite supportive infrastructure.
Balancing innovation with practicality: Ammonia-powered engines’ potential and limitations
In summary, this new ammonia-powered engine by GAC and Toyota is a good revolution that could help the automotive industry move away from carbon emissions. Thus, the brilliant results and the noticeable decrease in CO2 emissions in comparison with traditional cars prove that this technology is quite useful and has great potential for the search for effective and environmentally friendly means of transport.
However, there is a problem with ammonia as fuel; issues such as toxicity, technical complexity, and the lack of infrastructure to supply ammonia make ammonia inadequate for large-scale application in passenger vehicles. Thus, despite the fact this direction can be considered an important step, many efforts in research and development still need to be made to resolve certain issues connected with the safety and practicability of ammonia as the fuel for vehicles.