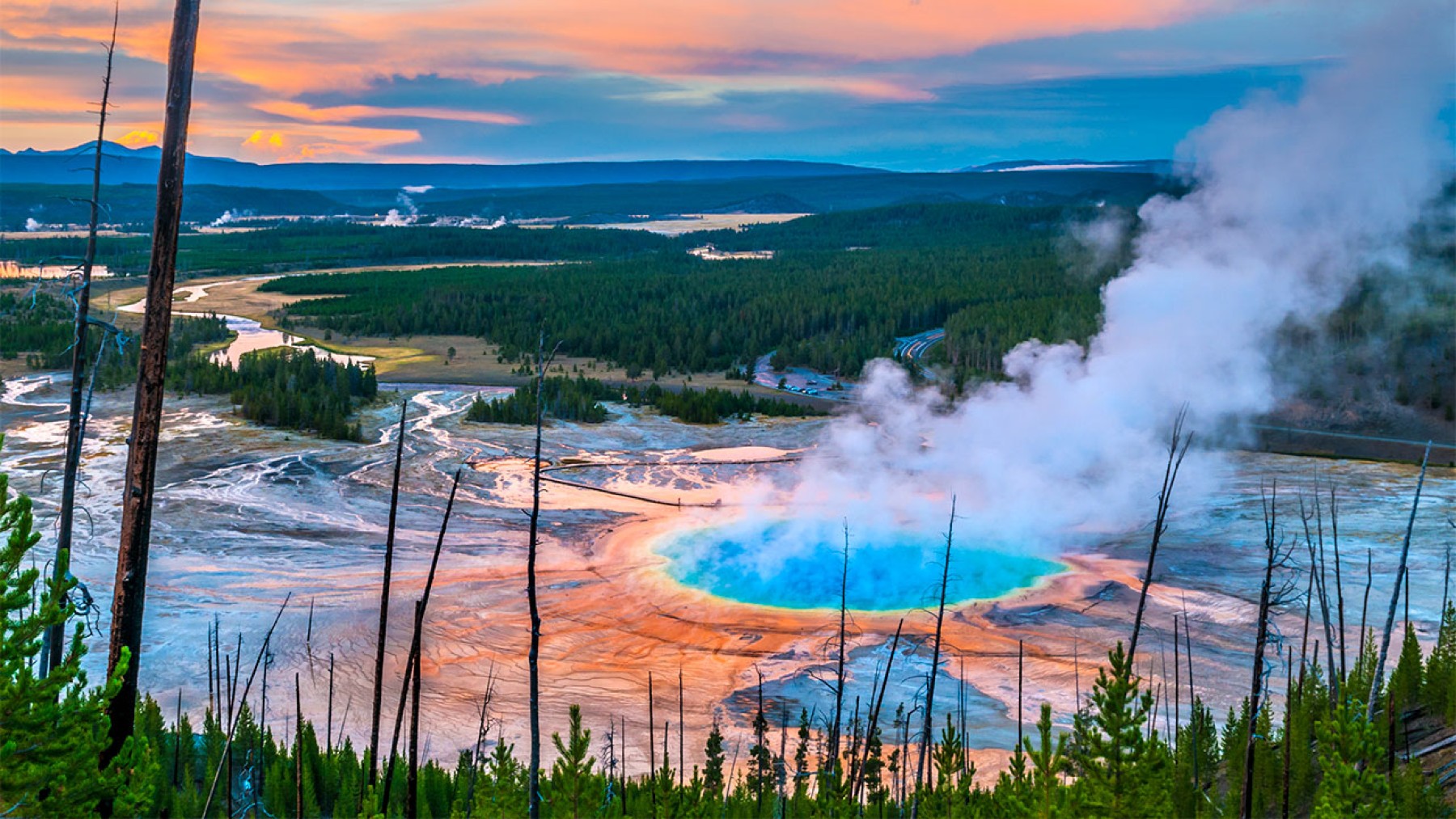
This park is primarily renowned for its natural wonders and splendid examples of wildlife, but now it has become the center of attention for a new, rather dangerous threat. Scientists have noted that climate change is at the precipice of fundamentally changing Yellowstone’s complex ecosystem.
Yellowstone Lake, the star of the Yellowstone ecosystem, is uniquely, perhaps dangerously, adaptable. That the lake’s ice cover has remained frozen for most of the year in the past three years may be concealing an underlying environmental threshold.
How Yellowstone Lake defies global warming with stability
Yellowstone Lake is also a high-altitude lake, but unlike most such lakes, it still can have ice in winter due to warming. This stability is quite different from that observed in many other North American and European lakes that have experienced a reduction in their ice cover season due to increasing global temperatures.
Scientists, however, are quick to point out that this so-called ‘resistance’ could crumble rather quickly as climate processes, especially precipitation, change. In light of this rise in temperature by 4.5 degrees F (2.5 degrees C) in Yellowstone Lake between 1980 and 2018, special attention has been given to the factors described here.
Hence, it is believed that a rise in the spring season’s snow rate has resulted in the stability of the ice cover in the lake, contrary to the expected effect of a warming trend. The snow thus shields the lake and the ice from early melting; the cumulative spring snow has been found to have doubled in the last one hundred years.
This is a somewhat different snowfall pattern than in other regions where snow has either not increased or remained stable. However, they said this buffer effect may not last long as the data indicated that people were not making much money. With climate change, it is even possible that it will start raining instead of snow, and the result is not as protective.
The lake’s tipping point: what rain-dominant seasons could mean
The decrease in the snow precipitation, especially during the fall and spring seasons, could take Yellowstone Lake to the precipice of a new regime of ice cover on the lake. The snowpack is necessary for ice formation and retention on Yellowstone Lake; failure to accrue enough snow may result in a shift in the freeze-thaw process of the lake, which may be permanent.
It only takes projections into the next decade to show that rain may start to dominate the cooler months, threatening the lake’s ice cover. Such a tipping point could be devastating in Yellowstone, having cascading effects on nearly all of the region’s resources, such as nutrients and fish.
Should the thickness of the ice be significantly diminished or, worse, should it vanish altogether from the face of Yellowstone’s Lake, the consequences would be severe. They would doubtless reverberate throughout the Yellowstone ecosystem. Ice is vital for nutrient cycling in the lake and the aquatic community’s productivity, which impacts wildlife across the park.
Lack of stable ice may affect fish spatial distribution and abundance, herbivores and other fauna, and recreational attractiveness – an essential feature of Yellowstone. The environmental and economic impacts may be severe because visitors and residents depend on this lake for fishing, boating, and overshadowing.
Global climate change pressures reveal Yellowstone’s delicate balance
Yellowstone’s problem is typical of what is happening to ecosystems worldwide. In light of climate change, the precipitation and temperature variability make ecosystems appear stable and vulnerable to sudden and irreversible changes.
The occurrence at Yellowstone is a good lesson on how climate change can be elegant and manifest in ways one least expects. As the global climate continues to warm, their potential to disrupt the delicate balances of ecosystems means that measures that need to be taken to reduce this impact and protect the ecosystems that may be most sensitive to climate change are more important than ever.
Recent stability in the ice over at Yellowstone Lake suggests drastic changes in the park’s climate and ecosystem may be just around the corner. When snow buffers wear off and rain appears more frequently, the region is on the verge of passing a point of no return.
Yellowstone is one of the stories in the big book of climate change, and everyone should embrace change to protect the Earth’s vulnerable ecosystems.